296. Best Meeting Point
Description
Given an m x n binary grid grid where each 1 marks the home of one friend, return the minimal total travel distance .
The total travel distance is the sum of the distances between the houses of the friends and the meeting point.
The distance is calculated using Manhattan Distance, where distance(p1, p2) = |p2.x - p1.x| + |p2.y - p1.y|.
Example 1:
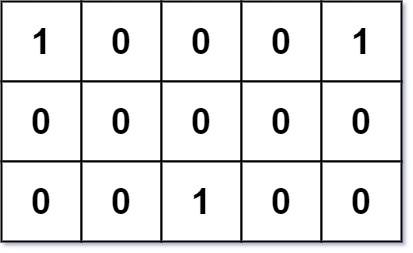
1 | Input: grid = [[1,0,0,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,1,0,0]] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: grid = [[1,1]] |
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 200grid[i][j]is either0or1.- There will be at least two friends in the
grid.
Hints/Notes
- 2025/02/26 Q2
- brain teaser
- Leetcode solution
Solution
Language: C++
1 | class Solution { |