272. Closest Binary Search Tree Value II
272. Closest Binary Search Tree Value II
Description
Given the root of a binary search tree, a target value, and an integer k, return the k values in the BST that are closest to the target. You may return the answer in any order .
You are guaranteed to have only one unique set of k values in the BST that are closest to the target.
Example 1:
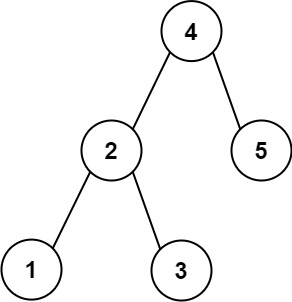
1 | Input: root = [4,2,5,1,3], target = 3.714286, k = 2 |
Example 2:
1 | Input: root = [1], target = 0.000000, k = 1 |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 1 <= k <= n <= 10^4.0 <= Node.val <= 10^9-10^9 <= target <= 10^9
Follow up: Assume that the BST is balanced. Could you solve it in less than O(n) runtime (where n = total nodes)?
Hints/Notes
- 2025/02/15 Q3
- BST
- Leetcode solution
Solution
Language: C++
1 | /** |