2116. Check if a Parentheses String Can Be Valid
2116. Check if a Parentheses String Can Be Valid
Description
A parentheses string is a non-empty string consisting only of '(' and ')'. It is valid if any of the following conditions is true :
- It is
(). - It can be written as
AB(Aconcatenated withB), whereAandBare valid parentheses strings. - It can be written as
(A), whereAis a valid parentheses string.
You are given a parentheses string s and a string locked, both of length n. locked is a binary string consisting only of '0's and '1's. For each index i of locked,
- If
locked[i]is'1', you cannot changes[i]. - But if
locked[i]is'0', you can changes[i]to either'('or')'.
Return true if you can make s a valid parentheses string. Otherwise, return false.
Example 1:
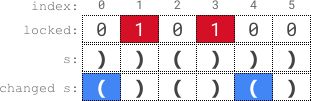
1 | Input: s = "))()))", locked = "010100" |
Example 3:
1 | Input: s = ")", locked = "0" |
Example 4:
1 | Input: s = "(((())(((())", locked = "111111010111" |
Constraints:
n == s.length == locked.length1 <= n <= 10^5s[i]is either'('or')'.locked[i]is either'0'or'1'.
Hints/Notes
- 2025/03/05 Q1
- stack
- Leetcode solution
Solution
Language: C++
1 | class Solution { |