1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix
1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix
Description
Given an n x n binary matrix grid, return the length of the shortest clear path in the matrix. If there is no clear path, return -1.
A clear path in a binary matrix is a path from the top-left cell (i.e., (0, 0)) to the bottom-right cell (i.e., (n - 1, n - 1)) such that:
- All the visited cells of the path are
0. - All the adjacent cells of the path are 8-directionally connected (i.e., they are different and they share an edge or a corner).
The length of a clear path is the number of visited cells of this path.
Example 1:
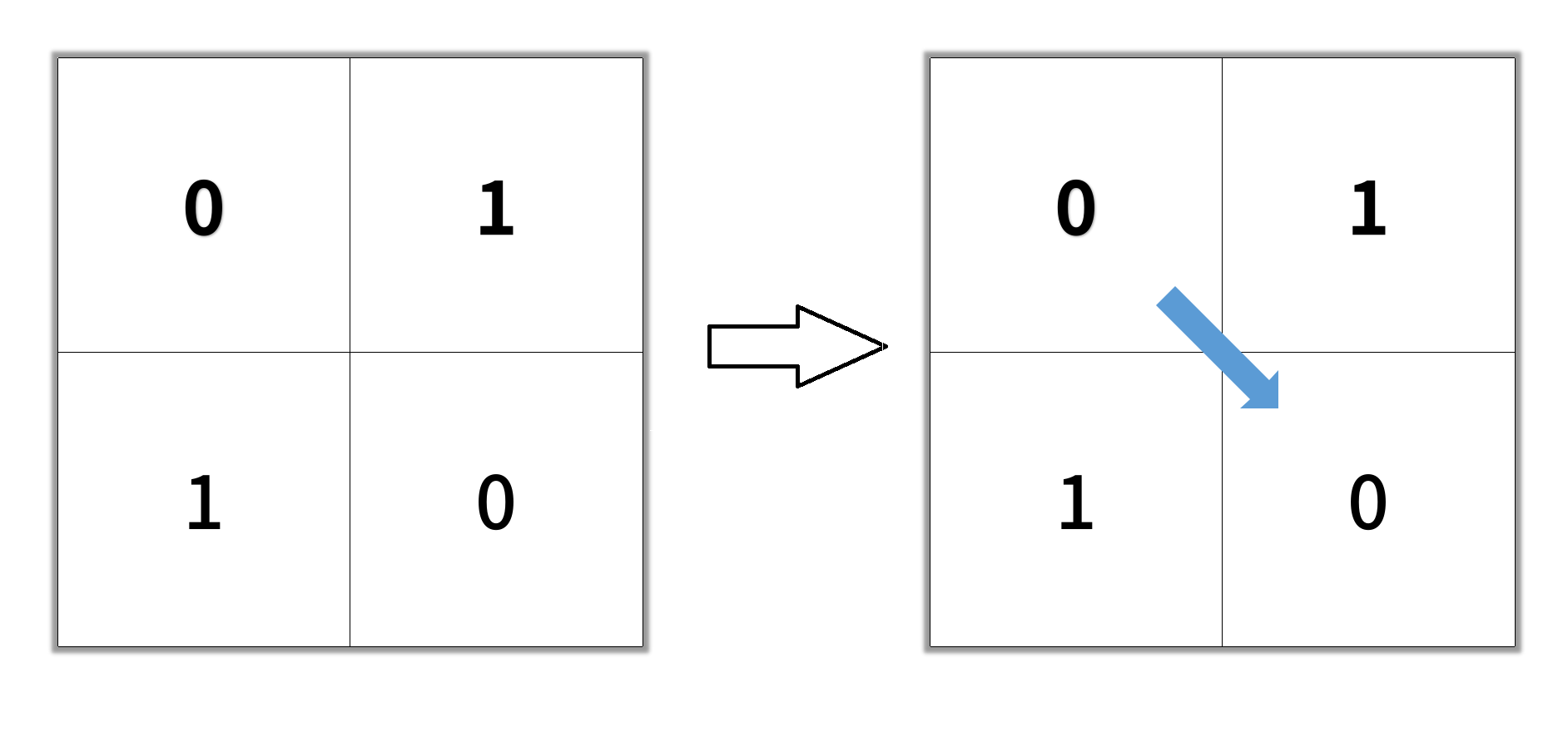
1 | Input: grid = [[0,1],[1,0]] |
Example 2:
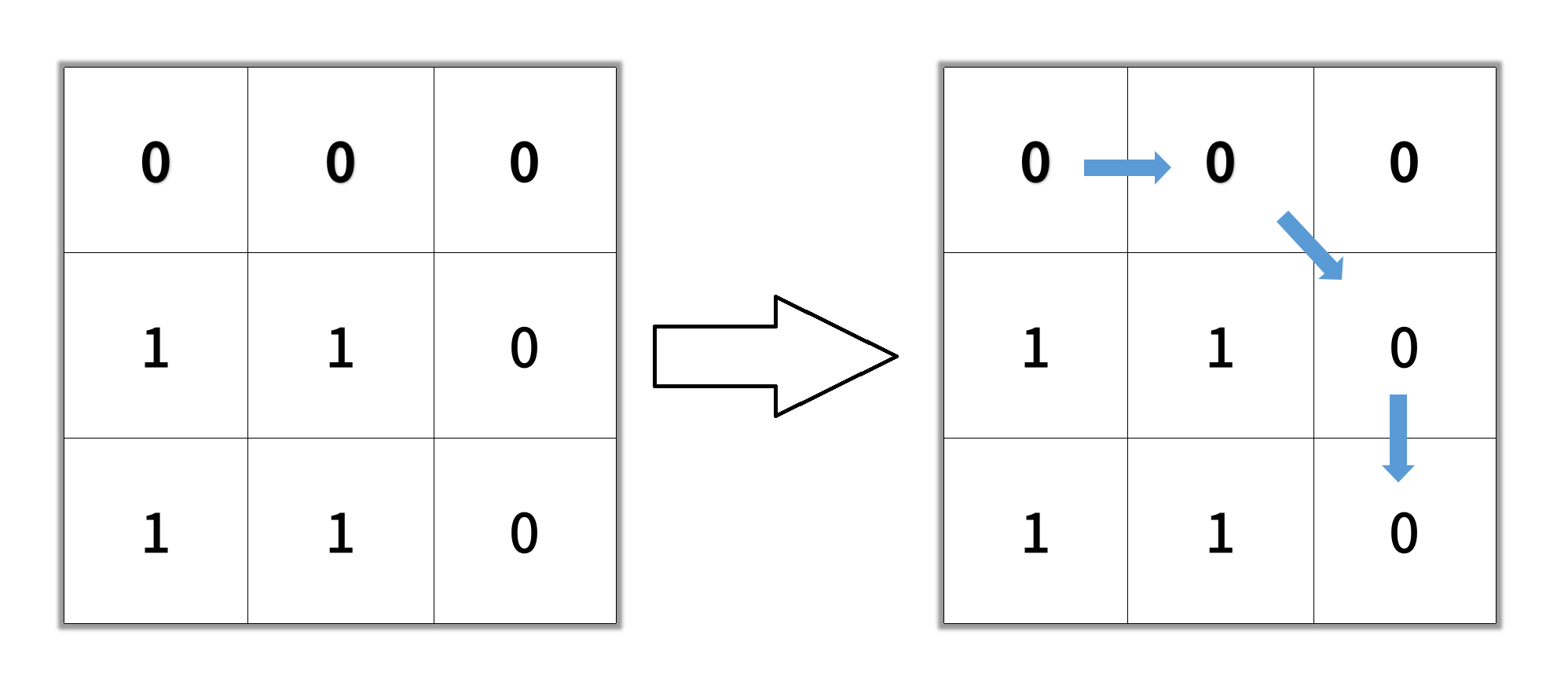
1 | Input: grid = [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: grid = [[1,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]] |
Constraints:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 100grid[i][j] is 0 or 1
Hints/Notes
- 2025/01/19
- bfs
- No solution from 0x3F
Solution
Language: C++
1 | class Solution { |