986. Interval List Intersections
986. Interval List Intersections
Description
You are given two lists of closed intervals, firstList and secondList, where firstList[i] = [starti, endi] and secondList[j] = [startj, endj]. Each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order .
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
A closed interval [a, b] (with a <= b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b.
The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that are either empty or represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].
Example 1:
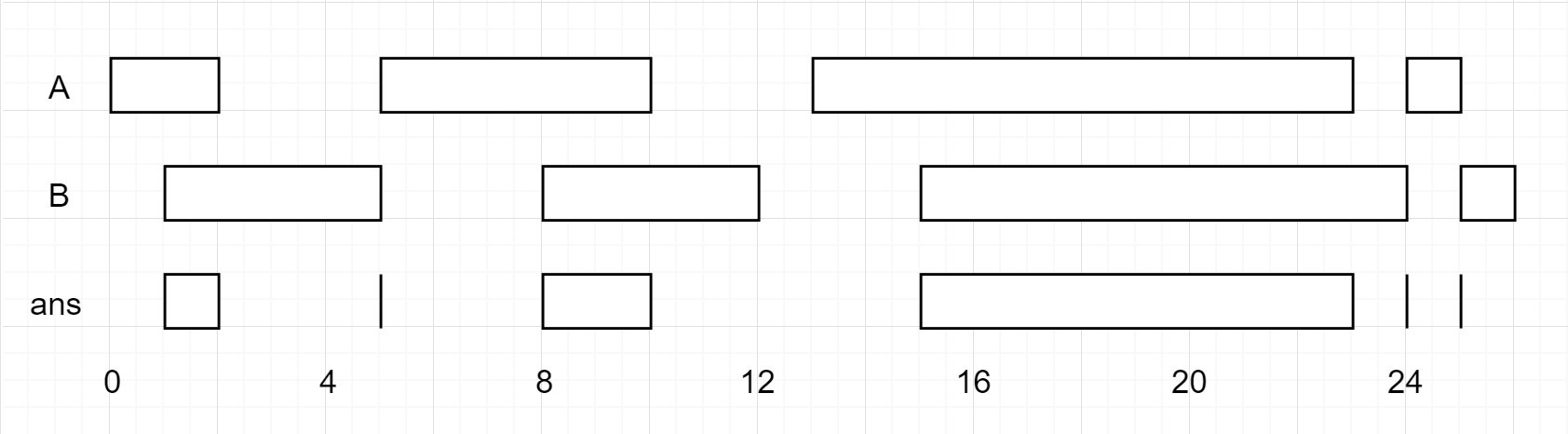
1 | Input: firstList = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], secondList = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: firstList = [[1,3],[5,9]], secondList = [] |
Constraints:
0 <= firstList.length, secondList.length <= 1000firstList.length + secondList.length >= 1- 0 <= starti < endi <= 10^9
- endi < starti+1
- 0 <= startj < endj <= 10^9
- endj < startj+1
Hints/Notes
- 2025/01/17
- Leetcode solution(checked)
Solution
Language: C++
1 | class Solution { |