3331. Find Subtree Sizes After Changes
3331. Find Subtree Sizes After Changes
Description
You are given a tree rooted at node 0 that consists of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The tree is represented by an array parent of size n, where parent[i] is the parent of node i. Since node 0 is the root, parent[0] == -1.
You are also given a string s of length n, where s[i] is the character assigned to node i.
We make the following changes on the tree one time simultaneously for all nodes x from 1 to n - 1:
- Find the closest node
yto nodexsuch thatyis an ancestor ofx, ands[x] == s[y]. - If node
ydoes not exist, do nothing. - Otherwise, remove the edge between
xand its current parent and make nodeythe new parent ofxby adding an edge between them.
Return an array answer of size n where answer[i] is the size of the subtree rooted at node i in the final tree.
Example 1:
1 | Input: parent = [-1,0,0,1,1,1], s = "abaabc" |
Explanation:
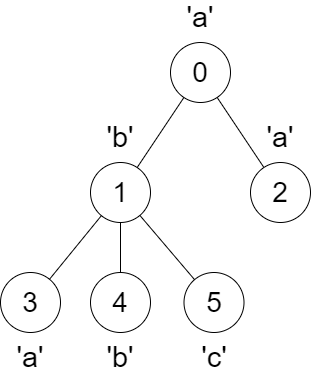
The parent of node 3 will change from node 1 to node 0.
Example 2:
1 | Input: parent = [-1,0,4,0,1], s = "abbba" |
Explanation:
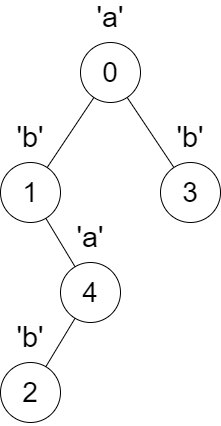
The following changes will happen at the same time:
- The parent of node 4 will change from node 1 to node 0.
- The parent of node 2 will change from node 4 to node 1.
Constraints:
n == parent.length == s.length1 <= n <= 10^50 <= parent[i] <= n - 1for alli >= 1.parent[0] == -1parentrepresents a valid tree.sconsists only of lowercase English letters.
Hints/Notes
- 2024/10/31
- Use array as map is faster
- 0x3F’s solution(checked)
- Biweekly Contest 142
Solution
Language: C++
One DFS
1 | class Solution { |
Two DFS:
1 | class Solution { |