3327. Check if DFS Strings Are Palindromes
3327. Check if DFS Strings Are Palindromes
Description
You are given a tree rooted at node 0, consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The tree is represented by an array parent of size n, where parent[i] is the parent of node i. Since node 0 is the root, parent[0] == -1.
You are also given a string s of length n, where s[i] is the character assigned to node i.
Consider an empty string dfsStr, and define a recursive function dfs(int x) that takes a node x as a parameter and performs the following steps in order:
- Iterate over each child
yofxin increasing order of their numbers , and calldfs(y). - Add the character
s[x]to the end of the stringdfsStr.
Note that dfsStr is shared across all recursive calls of dfs.
You need to find a boolean array answer of size n, where for each index i from 0 to n - 1, you do the following:
- Empty the string
dfsStrand calldfs(i). - If the resulting string
dfsStris a palindrome, then setanswer[i]totrue. Otherwise, setanswer[i]tofalse.
Return the array answer.
Example 1:
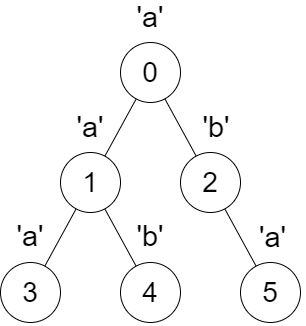
1 | Input: parent = [-1,0,0,1,1,2], s = "aababa" |
Explanation:
- Calling
dfs(0)results in the stringdfsStr = "abaaba", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(1)results in the stringdfsStr = "aba", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(2)results in the stringdfsStr = "ab", which is not a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(3)results in the stringdfsStr = "a", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(4)results in the stringdfsStr = "b", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(5)results in the stringdfsStr = "a", which is a palindrome.
Example 2:
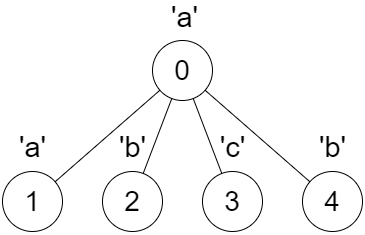
1 | Input: parent = [-1,0,0,0,0], s = "aabcb" |
Explanation:
Every call on dfs(x) results in a palindrome string.
Constraints:
n == parent.length == s.length1 <= n <= 10^50 <= parent[i] <= n - 1for alli >= 1.parent[0] == -1parentrepresents a valid tree.sconsists only of lowercase English letters.
Hints/Notes
- 2024/10/11
- Manacher’s algorithm
- 0x3F’s solution(checked)
- Weekly Contest 420
Solution
Language: C++
1 | class Solution { |