2090. K Radius Subarray Averages
2090. K Radius Subarray Averages
Description
You are given a 0-indexed array nums of n integers, and an integer k.
The k-radius average for a subarray of nums centered at some index i with the radius k is the average of all elements in nums between the indices i - k and i + k (inclusive ). If there are less than k elements before or after the index i, then the k-radius average is -1.
Build and return an array avgs of length n where avgs[i] is the k-radius average for the subarray centered at index i.
The average of x elements is the sum of the x elements divided by x, using integer division . The integer division truncates toward zero, which means losing its fractional part.
- For example, the average of four elements
2,3,1, and5is(2 + 3 + 1 + 5) / 4 = 11 / 4 = 2.75, which truncates to2.
Example 1:
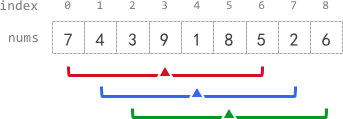
1 | Input: nums = [7,4,3,9,1,8,5,2,6], k = 3 |
Explanation:
- avg[0], avg[1], and avg[2] are -1 because there are less than k elements before each index.
- The sum of the subarray centered at index 3 with radius 3 is: 7 + 4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 = 37.
Using integer division , avg[3] = 37 / 7 = 5. - For the subarray centered at index 4, avg[4] = (4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2) / 7 = 4.
- For the subarray centered at index 5, avg[5] = (3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2 + 6) / 7 = 4.
- avg[6], avg[7], and avg[8] are -1 because there are less than k elements after each index.
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [100000], k = 0 |
Explanation:
- The sum of the subarray centered at index 0 with radius 0 is: 100000.
avg[0] = 100000 / 1 = 100000.
Example 3:
1 | Input: nums = [8], k = 100000 |
Explanation:
- avg[0] is -1 because there are less than k elements before and after index 0.
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 10^50 <= nums[i], k <= 10^5
Hints/Notes
- 2024/10/05
- sliding window
- No solution from 0x3F
Solution
Language: C++
1 | class Solution { |