1008. Construct Binary Search Tree from Preorder Traversal
1008. Construct Binary Search Tree from Preorder Traversal
Description
Given an array of integers preorder, which represents the preorder traversal of a BST (i.e., binary search tree), construct the tree and return its root.
It is guaranteed that there is always possible to find a binary search tree with the given requirements for the given test cases.
A binary search tree is a binary tree where for every node, any descendant of Node.left has a value strictly less than Node.val, and any descendant of Node.right has a value strictly greater than Node.val.
A preorder traversal of a binary tree displays the value of the node first, then traverses Node.left, then traverses Node.right.
Example 1:
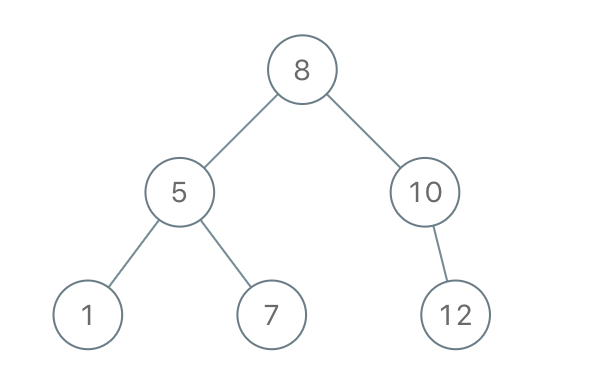
1 | Input: preorder = [8,5,1,7,10,12] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: preorder = [1,3] |
Constraints:
1 <= preorder.length <= 1001 <= preorder[i] <= 1000- All the values of
preorderare unique .
Hints/Notes
- 2024/07/03
- binary search tree
- No solution from 0x3F
Solution
Language: C++
1 | /** |