1325. Delete Leaves With a Given Value
1325. Delete Leaves With a Given Value
Description
Given a binary tree root and an integer target, delete all the leaf nodes with value target.
Note that once you delete a leaf node with value target, if its parent node becomes a leaf node and has the value target, it should also be deleted (you need to continue doing that until you cannot).
Example 1:
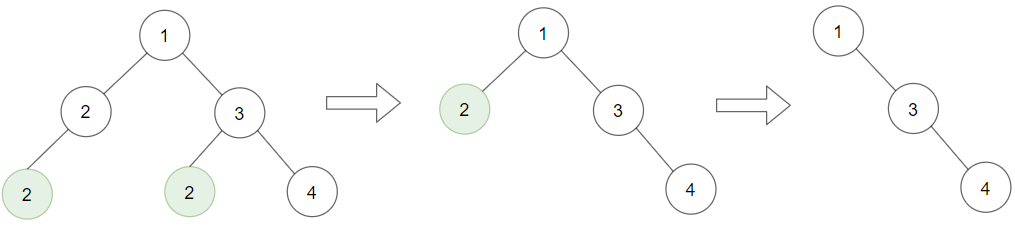
1 | Input: root = [1,2,3,2,null,2,4], target = 2 |
Example 2:
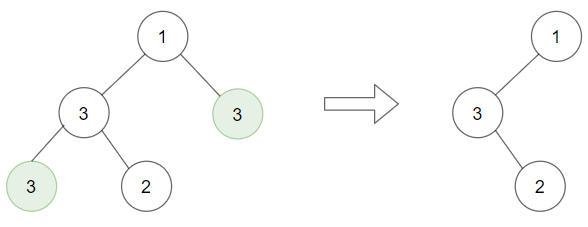
1 | Input: root = [1,3,3,3,2], target = 3 |
Example 3:
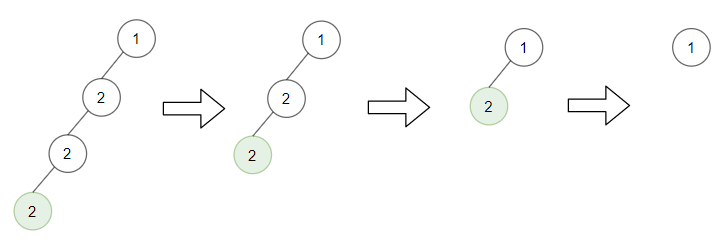
1 | Input: root = [1,2,null,2,null,2], target = 2 |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3000]. 1 <= Node.val, target <= 1000
Hints/Notes
- binary tree
Solution
Language: C++
1 | /** |