1261. Find Elements in a Contaminated Binary Tree
1261. Find Elements in a Contaminated Binary Tree
Description
Given a binary tree with the following rules:
root.val == 0- If
treeNode.val == xandtreeNode.left != null, thentreeNode.left.val == 2 * x + 1 - If
treeNode.val == xandtreeNode.right != null, thentreeNode.right.val == 2 * x + 2
Now the binary tree is contaminated, which means all treeNode.val have been changed to -1.
Implement the FindElements class:
FindElements(TreeNode* root)Initializes the object with a contaminated binary tree and recovers it.bool find(int target)Returnstrueif thetargetvalue exists in the recovered binary tree.
Example 1:
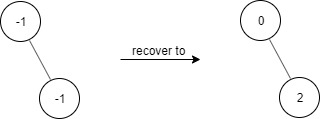
1 | Input: |
Example 2:
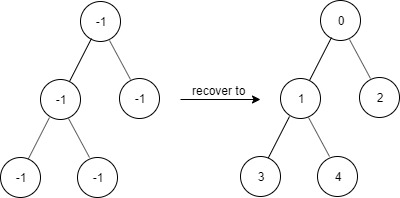
1 | Input: |
Example 3:
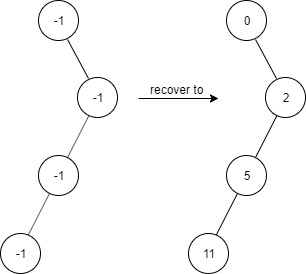
1 | Input: |
Constraints:
TreeNode.val == -1- The height of the binary tree is less than or equal to
20 - The total number of nodes is between
[1, 10^4] - Total calls of
find()is between[1, 10^4] 0 <= target <= 10^6
Hints/Notes
- N/A
Solution
Language: C++
1 | /** |