114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
Description
Difficulty: Medium
Related Topics: Linked List, Stack, Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Tree
Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a “linked list”:
- The “linked list” should use the same
TreeNodeclass where therightchild pointer points to the next node in the list and theleftchild pointer is alwaysnull. - The “linked list” should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
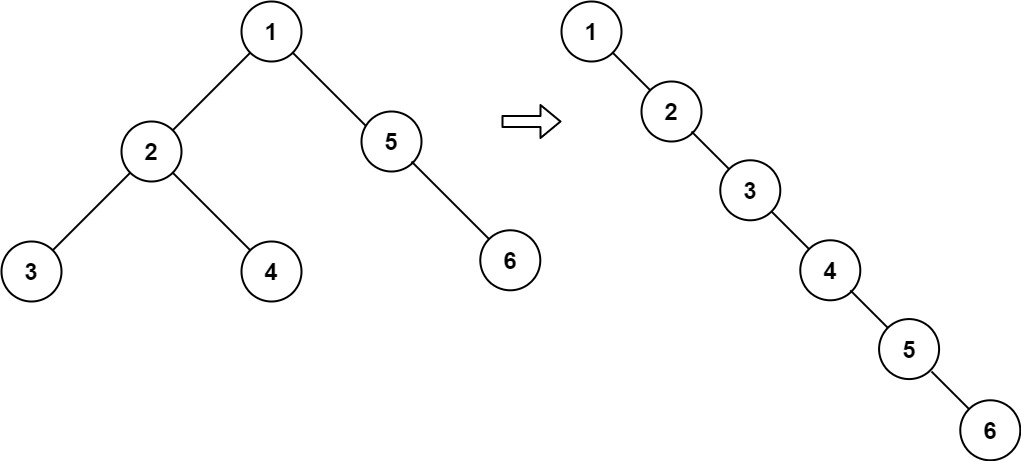
1 | Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: root = [] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: root = [0] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Can you flatten the tree in-place (with O(1) extra space)?
Hints/Notes
- 2023/08/16
- Recursive, think about if the left and right node has been flattened
- Leetcode solution(checked)
Solution
Language: C++
1 | /** |
With stack:
1 | /** |