92. Reverse Linked List II
Description
Difficulty: Medium
Related Topics: Linked List
Given the head of a singly linked list and two integers left and right where left <= right, reverse the nodes of the list from position left to position right, and return the reversed list.
Example 1:
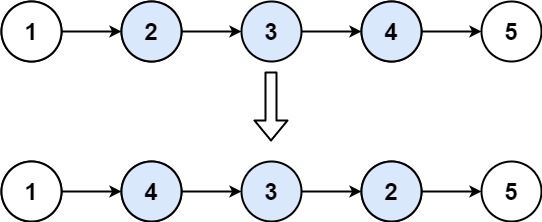
1 | Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4 |
Example 2:
1 | Input: head = [5], left = 1, right = 1 |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
n. 1 <= n <= 500-500 <= Node.val <= 5001 <= left <= right <= n
Follow up: Could you do it in one pass?
Hints/Notes
- Implement reverseN(reverse the fist N elements of one list) first,
i.e. reverseN(3) = 3->2->1->4->5
1 | class Solution { |
Solution
Language: C++
1 | /** |