86. Partition List
Description
Difficulty: Medium
Related Topics: Linked List, Two Pointers
Given the head of a linked list and a value x, partition it such that all nodes less than x come before nodes greater than or equal to x.
You should preserve the original relative order of the nodes in each of the two partitions.
Example 1:
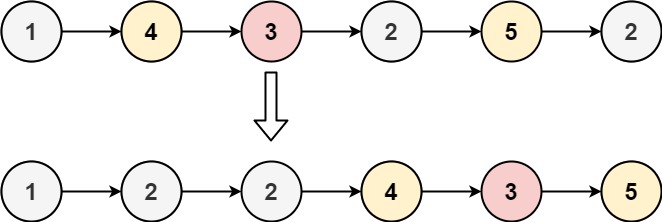
1 | Input: head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3 |
Example 2:
1 | Input: head = [2,1], x = 2 |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 200]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100-200 <= x <= 200
Hints/Notes
- Use two lists
- Break the link after the node is added to a new list
Solution
Language: C++
1 | /** |